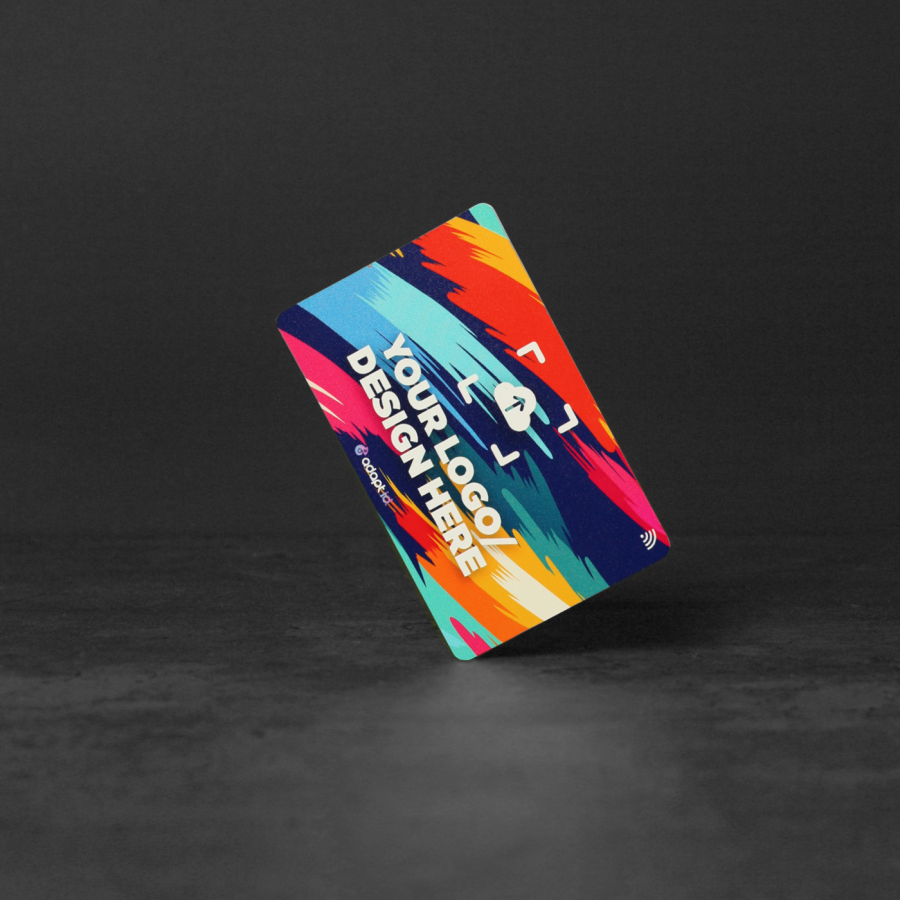
In today’s digital-first world, standing out in business networking means combining innovation with personalization. A bespoke contactless NFC business card by Adapt ID does exactly that—blending technology, design, and convenience into one powerful tool. Here’s how to create your own customised NFC business card with Adapt ID:
1. Choose Your Card Style and Finish
Adapt ID offers a wide range of premium materials and finishes - from sleek matte black and brushed metal to eco-friendly PLA and custom acrylics. Decide whether you want a traditional card size, a mini version, or something completely unique in shape and dimension.
You can also choose between printed, laser-engraved, or dual-layered designs for added flair.
2. Custom Design Your Branding
Work with Adapt ID’s in-house design team or provide your own artwork. Your card can feature your logo, social media icons, custom text, QR codes, and even embossed elements. Every detail from colour to layout is tailored to reflect your brand identity and professional presence.
3. Build Your Required Functionality
Adapt ID uses high-performance NFC chips programmed to launch your digital profile, website, contact form, vCard, or even custom smart-link pages.
You can choose whether the card is locked, rewritable, or managed via a cloud-based dashboard for future updates.
4. Add Smart Features
For an advanced user experience, you can opt for features such as:
Dual-chip (NFC + RFID) cards offer key card access alongside digital ID profiles, linking analytics tracking via Adapt ID’s platform.
Direct CMS integration with Hubspot, Dynamics 365 and 1000's of other direct API integration.
These options are ideal for professionals who want more than just a digital handshake - they want insight and control.
5. Test & Approve Your Card
Before final production, Adapt ID provides a proof for approval. Once approved, your card enters production and dispatched within 24 hours.
6. Start Networking Smarter
Once received, simply tap the card on any NFC-enabled smartphone and your digital profile or content will launch instantly—no app needed. You’ll impress clients, streamline follow-ups, and eliminate the need for paper cards.
Why Adapt ID?
Adapt ID leads the way in UK-made, contactless nfc business card solutions. With in-house production, custom engraving, dynamic NFC platforms, and enterprise options, they provide businesses and individuals with professional-grade networking tools tailored to the digital age.
Start your journey today by creating an nfc business card as unique as your brand.